Do hernias repair itself is a common question that many find themselves pondering upon diagnosis. Unfortunately, the answer is no. Hernias are completely self-limiting; the only way to get rid of them is through surgery.
Delaying treatment for painless hernias can lead to serious complications like strangulation or incarceration, where trapped tissue loses its blood supply.
Hernias are a common health issue that needs quick care for successful treatment. Some people choose to wait and see, but hernia surgery is usually needed for important reasons, to avoid problems and improve their lives.
If hernia symptoms are ignored, it can lead to serious consequences, especially if the blood supply to the tissues is affected. Knowing the different treatment options and the need for fast medical attention can help people make good choices for their health.
Key Highlights
- Hernias require surgical intervention as a treatment; they do not heal naturally.
- Postponing treatment for a hernia can results in serious issues such as strangulation or incarceration.
- The protrusion of an organ or tissue due to weakening of the surrounding muscles or connective tissue is known as a hernia.
- Advances in hernia surgery, including laparoscopic techniques, offer less pain and quicker recovery.
- Identifying symptoms such as hernia pain or visible swelling can help determine if immediate medical attention is needed.
- Consultation with an experienced healthcare provider is vital for exploring treatment options effectively.
Understanding Hernias: Basics and Importance of Treatment
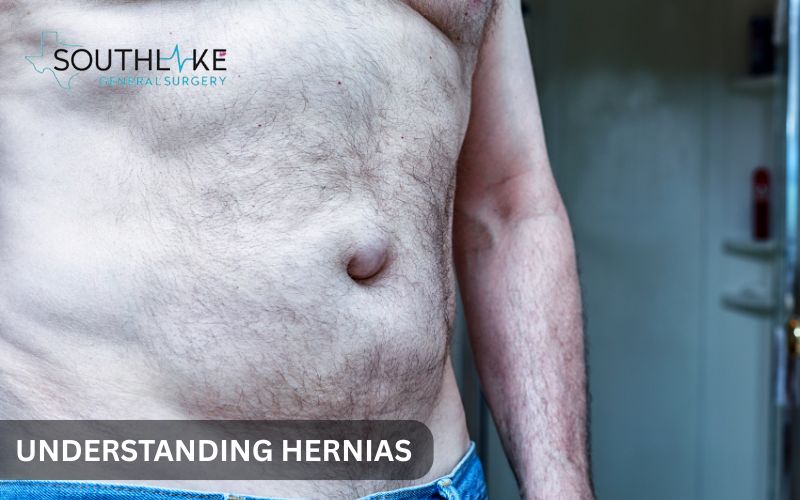
An unsightly and painful protrusion known as a hernia happens when an organ or piece of tissue pushes through a hole in the body’s connective tissues or muscles. They represent more than just physical issues; untreated hernias can escalate into serious health problems.
Timely treatment is crucial, as symptoms may initially seem mild but can worsen over time. Larger hernias increase the risk of complications like tissue strangulation or blockage, including the risk of a loop of intestine becoming trapped. Surgery is often required for a lasting solution.
What is a Hernia?
A hernia is a health problem where tissues or organs push through weak spots in the abdominal wall. This bulge happens when stress affects the connective tissue or muscle layers, particularly when the muscle wall of the belly is compromised. This may lead to a lack of stability in the impacted region.
Hernias usually happen when fatty tissue pushes through a weak area. These occurrences typically take place in the abdominal area or the groin region. You might feel discomfort, tenderness, and see noticeable swelling, which may go away after resting or moving.
Things like heavy lifting, getting older, or past injuries can weaken the muscle wall, making it easier for tissue bulges to form. Seeking an early diagnosis from a healthcare provider is crucial. You should look into repair options to prevent problems like strangulation or ongoing pain.
Why is Immediate Treatment Crucial?
Prompt treatment for hernias is very important to avoid serious risks. If not addressed, hernias may impede the circulation to adjacent tissues. This may lead to damage or potentially result in tissue necrosis. This critical matter is referred to as strangulation and requires immediate medical intervention.
Untreated hernias can also become incarcerated. It appears that the hernia has become stuck and cannot be moved. These situations increase the risk of complications and cause severe pain, so quick action is essential.
Getting treatment right away can help with ongoing problems like discomfort and limited movement. Hernia surgery can effectively stop severe pain and help you return to normal activities.
Your personal feelings about the procedure can also influence your decision. It also lowers risks for the future. It is best to consult healthcare professionals early on to deal with the problem.
Common Types of Hernias and Their Characteristics
Hernias come in different types, each with its own location and level of severity. Common types include inguinal hernias, primarily affecting men and occurring in the groin area. Femoral hernias usually affect women because of their body structure.
Other types include umbilical hernias, which show up around the belly button and are often present from birth. Incisional hernias happen when tissue is weak after surgery.
Knowing the type is important for doctors. It helps them decide on the right treatment, such as open surgery or laparoscopic hernia repair.
Inguinal Hernias
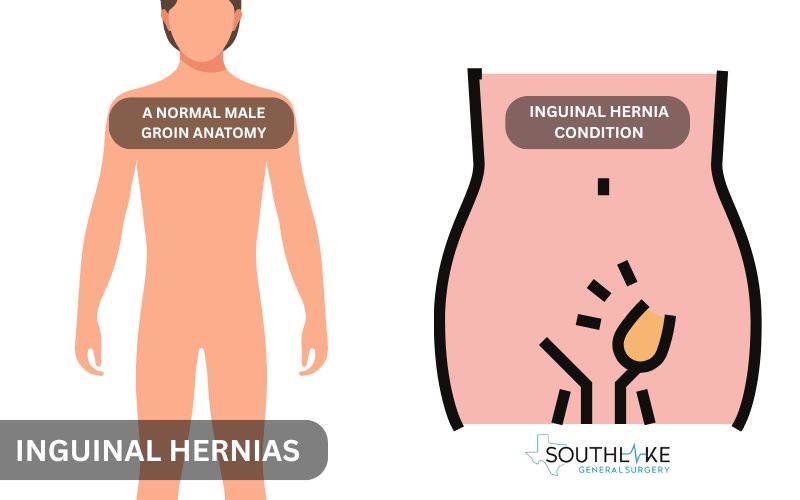
An inguinal hernia happens when tissue pushes through the inguinal canal, found in the groin area. This type of hernia is one of the specific types of hernias, accounting for 75% of all hernias, and it is more common in men because of their body structure.
Activities like heavy lifting or repeated strain can weaken the muscle wall. This allows parts of the intestine or fatty tissue to stick out. Symptoms usually include a visible bulge and pain that gets worse when you stand, bend, or lift things.
It’s important to address an inguinal hernia, as leaving it untreated may lead to it growing larger and causing increased discomfort over time. Surgery is needed to fix the hernia. You can choose between open hernia surgery and laparoscopic surgery for your procedure, giving you options that may suit your needs.
It helps to avoid serious issues like strangulation. Seeing a healthcare provider early can help detect and solve the problem quickly.
Femoral Hernias
Femoral hernias occur when loops of intestine or fatty tissue protrude through the femoral canal. This canal is under the inguinal canal. These hernias are not very common but mostly affect women. This is often because of their anatomy and reproductive factors.
It’s common for patients to experience pain or discomfort in a particular area, especially when there’s increased pressure in the abdomen, such as during a cough. In serious cases, there may be visible swelling that requires urgent medical attention if strangulation occurs.
Obesity and extra weight can make people more likely to get femoral hernias. Getting a surgical repair is important and often uses minimally invasive methods.
This helps stop the symptoms from getting worse and avoids complications. Talking to healthcare professionals is very helpful for getting tailored solutions for effective management.
Umbilical Hernias
Fat or a section of the intestines protrudes through the abdominal wall close to the belly button, a condition known as an umbilical hernia. These are common in newborns but can also happen to adults. Adults often get them due to strained connective tissue or after repeated pregnancies.
You can usually see umbilical hernias as soft bumps near the belly button. They might increase in size during periods of activity. At first, the pain or discomfort might be mild. However, if not addressed, it may result in significant issues, such as tissue death.
To fix an umbilical hernia, surgery is crucial. Umbilical hernia repair minimizes risks and restores stability. This allows people to return to their regular activities.
Healthcare professionals assess the severity of the hernia and determine the most effective approach for correction. This can be achieved via conventional open surgery or through advanced laparoscopic hernia surgery.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Surgical Intervention

Certain signs indicate that you should see a doctor for a hernia. If you experience pain or discomfort, especially if it affects your daily activities, do not ignore it.
Bulging or swelling is a strong sign that you may need surgical repair. Tender or discolored bulges may signal complications like incarceration, requiring immediate care. Recognizing these signs early ensures timely treatment and reduces risks associated with untreated hernias.
Pain and Discomfort
Persistent hernia pain is often the first symptom you notice. You might feel discomfort when you bend, stand up straight, or lift things. If the pain becomes severe and gets worse over time, it could be a sign of serious problems that need medical attention.
The pain can range from:
- Mild discomfort
- Sharp, stabbing feelings in the affected area
Straining during bowel movements or coughing can put more stress on the weak muscle wall, making the problem worse.
Talking to healthcare providers can help diagnose hernia pain. They can offer personalized treatment to reduce symptoms and prevent complications, helping you get back to your normal activities.
Visible Bulging or Swelling
Surgical repair of a hernia may be required if the bulge is painful or causes discomfort. This small bulge usually pops up when you do activities that require strain, like coughing or lifting. It might disappear when you recline.
As time goes by, these bulges can get bigger and harder to push back inside. If you notice discoloration, tenderness, or swelling, these could mean serious problems like incarceration. This situation needs urgent surgery.
Talking about visible lumps with a healthcare provider is important. They can help identify the issue and arrange for repair quickly. This can lower the risks that come from untreated hernias and help relieve symptoms effectively.
Risks of Not Treating a Hernia
Ignoring hernias can make things worse. It raises the possibility of complications like incarceration or strangulation. These problems happen when tissue gets stuck or doesn’t get enough blood supply, leading to blockages in the intestines or tissue death.
Besides causing physical discomfort, not treating hernias may affect daily activities due to pain. Seeking medical advice is crucial to mitigate these risks. This helps ensure proper repair and long-lasting relief.
Risk of Incarceration
Incarceration happens when hernia tissue gets stuck and cannot go back into the stomach area. This can lead to serious problems and often comes with severe pain in the affected area.
An increased risk of incarceration can block food and gas from moving through the intestines. This causes more discomfort, especially if not handled quickly. That’s why early detection and talking to healthcare providers is so important.
Doctors suggest surgery to stop the risks of incarceration. This plan helps with a smoother recovery and lowers the chance of future problems with incarcerated hernias.
Risk of Strangulation
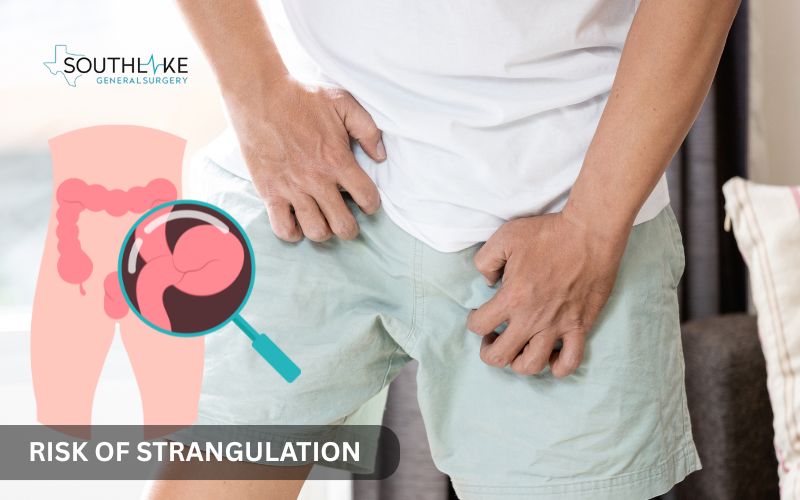
Strangulation can be one of the most serious problems caused by untreated hernias. It happens when the blood supply to the affected tissues is cut off, leading to tissue death. This situation is a medical emergency. It needs quick action to prevent serious, long-lasting harm.
When tissue strangulation occurs, you may experience symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, and intense pain in a specific area. If not treated, this can lead to necrosis, which is irreversible tissue death. This can be life-threatening without surgery.
Choosing to have hernia surgery quickly removes the risk of strangulation. It helps restore blood supply, fixes the weakened area, and avoids serious health problems.
Advances in Hernia Surgery
The effectiveness of hernia repairs has increased thanks to advancements in modern surgical methods. Laparoscopic surgery uses small incisions and advanced surgical tools. This greatly reduces recovery time.
Both robotic and laparoscopic hernia repair techniques reduce the intensity of pain experienced after surgery. They also effectively tackle different types of hernias. Healthcare experts use advanced technologies to meet the unique needs of each patient for the best success rates.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery involve making small incisions on the exterior of the body. This helps doctors access and fix hernias effectively. They use tiny cameras and surgical tools to cause less injury during the surgery.
This method also leads to less visible scarring and less pain after the procedure, which helps most patients recover faster. It works particularly well for fixing complex hernias, such as inguinal or femoral hernias.
Using these minimally invasive methods, along with synthetic mesh, helps strengthen the muscle wall. This minimizes the possibility of the hernia recurring and provides enduring support.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic hernia repair has clear benefits:
- Causes less pain than regular surgery.
- Patients often recover faster and can return to their normal activities in about four weeks.
- Minimizes the chances of complications, including infections or bleeding.
- Smaller incisions result in less scarring after surgery, which many people prefer for cosmetic reasons.
Medical professionals frequently recommend minimally invasive surgery as it efficiently addresses persistent hernia symptoms and mitigates the risk of strangulation. A personal consultation helps to choose the best option for each person’s situation.
Preparing for Hernia Surgery
Surgical preparation begins with a session with a healthcare provider. Dr. Valeria Simone, an expert in her field, guides patients through their treatment plans for specific hernias.
Patients are better prepared for surgery if they know what to expect during the procedure and recuperation phase. Open communication builds confidence and allows for discussion of personal health concerns.
Consultation with Dr. Valeria Simone
Dr. Valeria Simone is a seasoned healthcare provider with extensive experience in the treatment of hernias. She offers personalized consultations so patients can learn about the best surgical methods for their specific type of hernia.
During visits, she discusses symptoms like visible bulging and severe pain. These are important when deciding on treatment options, including minimally invasive or traditional methods. Dr. Simone carefully reviews the risks and benefits to help patients make informed choices, providing a record of your answers for future reference.
Patients should reach out to Southlake General Surgery in Texas for scheduling and professional advice. This helps ensure they have a positive healthcare experience.
What to Expect Before, During, and After Hernia Repair Surgery
Before surgery, doctors check and perform imaging tests, including a CT scan, to find out the type and seriousness of the hernia. This helps surgeons make a plan. Patients will get instructions on how to prepare, like what to eat or avoid.
The surgical process involves repositioning and securing the misplaced tissue with stitches or a synthetic patch or mesh. This helps make sure the fix lasts. Less time spent in the operating room and less pain during surgery are two benefits of modern laparoscopic techniques.
After surgery, care focuses on watching how well the patient recovers. This includes taking time to rest and slowly adding physical activities back in. Follow-up visits help address any worries and make it easier for patients to get back to their normal lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, some people might wonder if hernias can fix themselves. The truth is, hernias usually do not get better without surgery. Quick treatment is possible if you know what a hernia is and how to recognize its symptoms.
Ignoring a hernia can lead to serious problems like incarceration or strangulation, which can be dangerous to your health. New surgical methods, like laparoscopic surgery, provide effective options with shorter recovery times. If you suspect you may be dealing with a hernia problem and encounter any of the following symptoms, do not hesitate to seek the advice of a medical professional.
Dr. Valeria Simone at Southlake General Surgery is here to support you on your journey to healing. Don’t wait— reach out and book an appointment today for personalized care and expert help. Your health is important, and taking action is the first step towards a better life.
Make an Appointment
Seeing a skilled healthcare provider is very important when dealing with a hernia. Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, is here to provide you with a thorough check-up tailored to the specific type of hernia you have.
Her team uses advanced methods like laparoscopic surgery and other options that are less invasive. This helps them perform surgical repair to reduce symptoms such as hernia pain or lumps that you can see.
Don’t wait to get medical attention; call +1 (817) 748-0200 to make an appointment. You will get expert advice on treatment options and how to manage your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a hernia repair itself without surgery?
No, hernias cannot heal by themselves. They need surgical repair to fix the tissue that is bulging through weak muscles. Waiting too long for surgery is not a good idea, especially in severe cases.
What are the signs that my hernia is getting worse?
Signs that a hernia is getting worse include more pain, larger lumps, or sharp pain during regular, intense activities. If you see a tender or discolored bulge in the area of the hernia, you should get medical attention right away. This can help avoid more serious problems, like strangulation.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- About your abdominal incisional hernia surgery. (n.d.). Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/patient-education/about-your-abdominal-incisional-hernia-surgery
- Hernia surgery Benefits, risks, and what to expect | UPMC. (n.d.). UPMC | Life Changing Medicine. https://www.upmc.com/services/general-surgery-trauma/services/hernia-surgery
- Conze J, Klinge U, Schumpelick V. Hernias. In: Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA, editors. Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Munich: Zuckschwerdt; 2001. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6888
- Inguinal hernia repair: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. (n.d.). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007406.htm
- Website, N. (2025b, April 15). Inguinal hernia repair. nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/inguinal-hernia-repair/
- Haladu, N., Alabi, A., Brazzelli, M., Imamura, M., Ahmed, I., Ramsay, G., & Scott, N. W. (2022c). Open versus laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia: an overview of systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials. Surgical Endoscopy, 36(7), 4685–4700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09161-6

