Graves’ disease is a chronic autoimmune condition that specifically targets the thyroid gland, resulting in its dysfunction. The condition is commonly referred to as Graves’ disease, named in honor of Sir Robert Graves, a distinguished Irish physician who initially documented this medical condition during the early 19th century.
This disease is characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus normally exert strict control over the production of thyroid hormones.

However, in Graves’ disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to become overactive. As a result, excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are released into the bloodstream.
This hormonal imbalance can have widespread effects on various organs and systems in the body. Some common symptoms of Graves’ disease include weight loss, increased appetite, fatigue, irritability, and heat intolerance. Excessive levels of thyroid hormones can also lead to an increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and an enlarged thyroid gland.
If left untreated, Graves’ disease can have serious complications, such as osteoporosis, eye problems, and even heart problems. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to managing the symptoms and preventing long-term complications.
Symptoms That Signal Graves’ Disease
The symptoms of this condition encompass a spectrum, from subtle to pronounced. Individuals might experience:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite unchanged dietary habits.
- Elevated Heart Rate: Irregular heartbeat or palpitations.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Unexplained exhaustion.
- Anxiety and Irritability: Heightened emotional responses.
- Heat Sensitivity: Intolerance to heat.
- Eye Problems: Bulging eyes, redness, or vision changes.
- Thyroid Enlargement: Swelling in the neck, known as goiter.
Spotting Graves’ Disease: The Diagnostic Journey
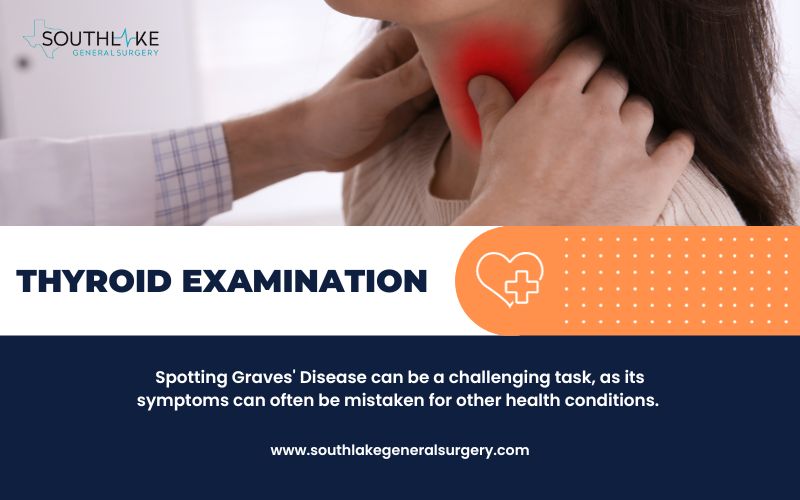
Spotting Graves’ Disease can be a challenging task, as its symptoms can often be mistaken for other health conditions. However, being aware of the common signs and symptoms can help in early detection and prompt treatment.
Diagnosing Graves’ Disease involves comprehensive evaluations, including:
1. Medical history review: The doctor will ask about any symptoms you have been experiencing and your family’s medical history.
2. Physical examination: The doctor will examine your neck for any signs of thyroid enlargement, such as a goiter.
3. Blood tests: These may include thyroid function tests to check the levels of thyroid hormones in your blood, as well as tests to check for specific antibodies associated with Graves’ disease.
4. Radioactive iodine uptake test: This test gauges how much radioactive iodine the thyroid gland absorbs, which can reveal whether it is overactive.
5. Thyroid ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland and can help identify any abnormalities or nodules.
6. Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to determine if any nodules or abnormalities found in the thyroid gland are cancerous. This involves removing a small sample of tissue from the thyroid for further analysis.
These tests are important in diagnosing Graves’ Disease and determining the appropriate course of treatment. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the results and plan the best treatment approach for managing the condition.
Treatment for Graves’ Disease
Treatment for Graves’ Disease typically involves a combination of medication, radioactive iodine therapy, and, in some cases, thyroid surgery. The goal of treatment is to control the overproduction of thyroid hormones and alleviate symptoms.
Graves’ Disease Medicines
Antithyroid drugs like methimazole or propylthiouracil may be used to treat Graves’ disease. These drugs stop the production of thyroid hormones. These medications are often prescribed initially to help manage symptoms and bring hormone levels back to normal.
In some cases, beta-blockers may also be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and tremors. It is important to take medication as prescribed and attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional to monitor hormone levels and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy

It is another treatment option for hyperthyroidism. It involves taking a small dose of radioactive iodine, which the overactive thyroid gland then absorbs. The radiation from the iodine destroys the thyroid cells, reducing the production of thyroid hormones.
This treatment is typically done as a one-time procedure and may result in hypothyroidism, requiring lifelong hormone replacement therapy. However, it is highly effective in treating hyperthyroidism and can provide long-term relief from symptoms.
Thyroid Surgery
Another treatment option for hyperthyroidism is thyroid surgery. This involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland to prevent the overproduction of thyroid hormones.

Thyroid surgery is typically recommended for individuals who have a large goiter or nodules on their thyroid, or for those who cannot tolerate or have not had success with other treatment options.
While it is an effective treatment, there are potential risks and complications associated with surgery, such as damage to the vocal cords or parathyroid glands.
Types of Thyroid Surgery
Several types of thyroid surgery may be performed, depending on the specific condition and needs of the patient.
The most common type is a total thyroidectomy, which involves the complete removal of the thyroid gland. This is often recommended for individuals with thyroid cancer or severe thyroid disorders.
Another type of surgery is a partial thyroidectomy, where only a portion of the thyroid gland is removed. This may be done for individuals with smaller nodules or goiters that do not require complete removal.
Additionally, there is a procedure called a thyroid lobectomy, which involves removing only one lobe of the thyroid gland. This is usually done when there are suspicious nodules or tumors in just one lobe, and the remaining lobe can continue to function properly.
It is important for doctors to carefully evaluate each individual case and determine the most appropriate type of surgery based on the specific condition and needs of the patient.
The goal of these surgeries is to effectively treat the thyroid disorder or cancer while minimizing potential complications and preserving the overall thyroid function.
Managing Graves’ Disease Holistically

In addition to surgical options, there are also holistic approaches to managing Graves’ Disease. These approaches focus on addressing the underlying causes of the condition and promoting overall health and well-being. This may involve implementing adjustments to one’s lifestyle, such as:
- Stress reduction techniques: Practicing stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help manage Graves’ Disease holistically.
- Dietary modifications: Making dietary modifications, such as reducing or eliminating gluten and sugar, can support overall thyroid function and manage Graves’ Disease holistically.
- Supplementation: Taking certain supplements, such as selenium or vitamin D, may help support thyroid health and manage Graves’ Disease holistically.
- Balancing hormones: Working with a healthcare professional to balance hormones through natural methods, such as herbal remedies or bioidentical hormone replacement therapy, can help manage Graves’ Disease holistically.
- Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help manage Graves’ Disease holistically by reducing stress, improving overall health, and supporting thyroid function.
Additionally, alternative therapies such as acupuncture and herbal remedies have shown promising results in managing the symptoms of Graves’ Disease.
Individuals with this condition need to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best course of action for their specific needs and goals.
The Prognosis
The prognosis for Graves’ Disease varies depending on the individual and their specific circumstances. In many cases, with proper management and treatment, individuals with Graves’ Disease can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. However, it is important to note that Graves’ Disease is a chronic condition and may require ongoing monitoring and treatment to maintain optimal health.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are essential to ensure that the condition is being effectively managed and any potential complications are addressed promptly.
With the right support and care, individuals with this medical condition can successfully navigate their journey towards improved health and well-being.
Seeking Expert Guidance

One important step in managing Graves’ Disease is seeking expert guidance from healthcare professionals who specialize in endocrine disorders.
These specialists, such as endocrinologists, can provide comprehensive evaluations, accurate diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans tailored to everyone’s specific needs. They have the knowledge and expertise to monitor hormone levels, assess symptoms, and adjust medications as necessary.
Additionally, they can offer guidance on lifestyle modifications, such as stress management and dietary changes, that can help alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being.
By working closely with these experts, individuals with this medical condition can feel confident in their treatment plan and achieve optimal health outcomes. This collaborative approach can lead to more effective and sustainable results. It can also improve the overall quality of life for individuals with Graves’ Disease.
Appointment

For more information on Graves’ Disease – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment or to book a consultation with Dr. Valeria Simone MD, at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA. You can contact our healthcare expert today for a quick appointment at +1 (817) 748-0200.
FAQ’s on Graves’ Disease
Here are some frequently asked questions about this condition:
1. What is Graves’ Disease, and how does it differ from other thyroid disorders?
Graves’ Disease is a condition where the immune system mistakenly causes the thyroid gland to become overactive. This results in the production of too many thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism is a unique thyroid disorder that is caused by an immune system malfunction attacking the thyroid. The condition is characterized by a diverse array of symptoms.
2. What are the key symptoms indicating Graves’ Disease?
Common symptoms include weight loss, increased appetite, anxiety, irritability, tremors, heat intolerance, sweating, and irregular menstrual periods. This condition can also cause bulging eyes, a condition known as exophthalmos.
3. How is Graves’ Disease diagnosed?
Graves’ Disease is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The doctor may conduct blood tests to measure levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3). They may also perform imaging tests such as a thyroid scan or ultrasound to evaluate the size and function of the thyroid gland. Additionally, an eye examination may be done to check for signs of exophthalmos.
4. Can Graves’ Disease be managed without medications?
Medications such as anti-thyroid drugs are important for managing hormone levels, but it’s worth noting that lifestyle changes can also have a significant impact on the condition. Proper nutrition, stress management, and regular monitoring are important aspects of holistic management.
5. What are the treatment options available for Graves’ Disease?
Thyroid conditions encompass a range of diseases, and fortunately, there exists an extensive range of treatment options to address these concerns. One option is to take anti-thyroid medications, which can help limit the production of hormones.
Another option is radioactive iodine therapy, which can reduce the activity of the thyroid. In some cases, a surgical procedure called thyroidectomy may be recommended to remove the thyroid gland.
These treatment avenues can be discussed with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your specific situation. Each approach considers individual health factors and uniquely addresses the condition.
6. Are there specific dietary considerations for individuals with Graves’ Disease?
It’s important to maintain a balanced iodine intake to support healthy thyroid function. Both excessive and insufficient amounts of iodine can have an impact on your thyroid. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to receive personalized dietary advice that suits your individual needs.
7. What is the long-term outlook for someone with Graves’ Disease?
Many individuals can lead healthy lives with proper management and treatment adherence. Regular monitoring, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking timely medical interventions can greatly improve your prognosis and enhance your overall quality of life.
8. Can Graves’ Disease affect pregnancy or fertility?
It’s important to be aware that if this condition is left untreated or not properly managed, it can potentially pose risks during pregnancy. Receiving specialized care is extremely important for pregnant individuals with this condition. It can have an impact on the development of the fetus and increase the risk of complications.
9. How important is it to seek medical advice for Graves’ Disease?
It is important to consult with an endocrinologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing management of your condition. Their expertise will help ensure that you receive the best possible care, tailored to your specific needs. Our team of experts is here to provide you with the guidance you need to effectively control your symptoms and minimize any potential complications.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References
- Graves’ Disease. (2022, November 16). National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/graves-disease
- DeGroot, L. J. (2016, November 2). Diagnosis and Treatment of Graves’ Disease. Endotext – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK285548/
- Menconi, F., Marcocci, C., & Marinò, M. (2014, April 1). Diagnosis and classification of Graves’ disease. Autoimmunity Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.013
- Hyperthyroidism. (n.d.). Graves’ Disease | Overactive Thyroid | MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/hyperthyroidism.html
- Healing of Graves’ Disease Thorough Lifestyle Changes: A Case Report. (2019). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31476135/

